Understanding rugby positions is essential for players and fans alike. Rugby is a sport built on teamwork, strategy, and individual skill, and each rugby position has specific responsibilities that influence the flow of the game. From the physically dominant forwards to the agile, tactical backs, every position is designed to maximise team performance and impact. Following England Rugby, Scotland Rugby, or Wales Rugby matches is far more engaging when you understand how each rugby position functions on the field.
Rugby positions also enhance a fan’s appreciation of major tournaments such as the Rugby World Cup 2025, Women’s Rugby World Cup, or Rugby Six Nations. Knowing who is responsible for winning scrums, creating attacking plays, or covering defensive gaps makes watching rugby today far more rewarding. Even keeping track of rugby scores and rugby fixtures is easier when you can identify the roles and contributions of players in each rugby position.
Overview of Rugby Union Gameplay
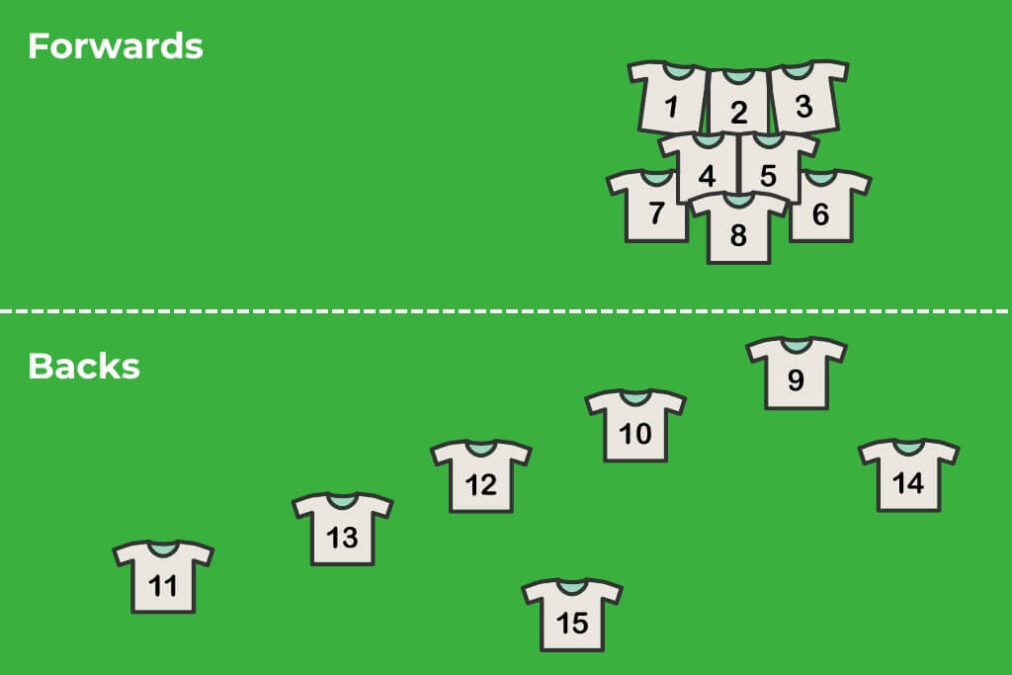
Rugby positions are broadly divided into forwards and backs, each with distinct responsibilities that influence the team’s strategy. Forwards are generally bigger and stronger, focusing on scrums, lineouts, and physical contests to secure the ball. Backs are usually quicker and more agile, specialising in passing, tactical kicking, and scoring tries. Understanding rugby positions helps fans follow BBC Rugby and BBC Sport Rugby coverage with greater clarity, especially during high-intensity games in the Rugby World Cup final or domestic leagues such as Bath Rugby.
The organisation of rugby positions also determines how a team responds to different game situations. Effective coordination between forwards and backs is essential for maintaining possession and executing attacking strategies. Observing how each rugby position contributes to scrums, rucks, mauls, or counter-attacks provides insight into team dynamics and explains why certain teams, like Ireland Rugby, dominate in both domestic and international competitions.
Forwards: Key Rugby Positions for Physical Play
Forwards play a vital role in controlling the physical side of rugby, and understanding rugby positions within this group is essential. These positions include the front row, second row, and back row, each contributing to set-piece dominance and open play. Players in forward rugby positions must combine strength, endurance, and tactical awareness to support their team in both attack and defence. Their work often goes unnoticed but is crucial for winning scrums and securing ball possession.
Front row rugby positions, including props and hookers, are responsible for stability and control in scrums. Props provide strength on either side of the hooker, who manages the ball during the scrum. Second row players, or locks, excel in lineouts and physical battles, while back row players, such as flankers and number eights, link the forwards and backs, securing the ball and supporting attacking plays. Understanding these rugby positions is essential for appreciating the structure and strategy of the game.
Backs: Crucial Rugby Positions for Speed and Strategy
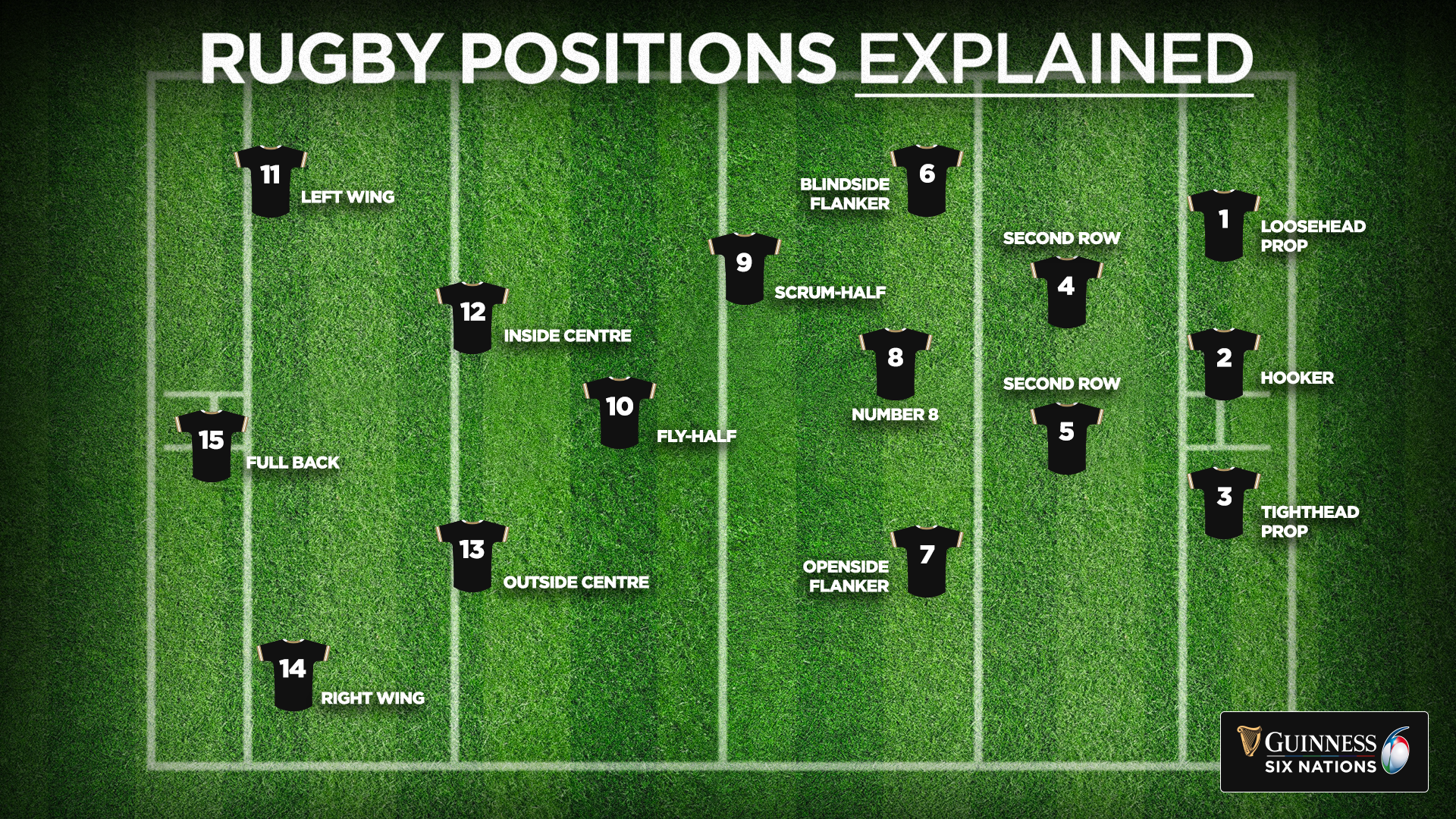
Backs are responsible for creating opportunities and scoring points, and knowledge of these rugby positions enhances understanding of team tactics. Positions in the backline include scrum-half, fly-half, centres, wingers, and fullback. Each role requires agility, speed, and decision-making skills to exploit space and maintain defensive coverage. Observing these rugby positions during high-level tournaments like Rugby Six Nations or the Rugby World Cup 2025 shows how tactical play shapes outcomes on the field.
Scrum-halves control the link between forwards and backs, feeding the ball to the fly-half, who often dictates attacking strategies. Centres combine strength and speed to penetrate defensive lines, while wingers use pace to finish scoring opportunities. Fullbacks are the last line of defence, managing kicks and organising the backfield. Knowledge of these rugby positions allows fans following BBC Rugby or checking rugby league scores to understand how strategic decisions are executed during a match.
Women’s Rugby Positions
Rugby positions in women’s rugby mirror the men’s game, but with some tactical differences that emphasise speed, agility, and teamwork. Understanding these rugby positions enhances appreciation for the growing prominence of women’s rugby, including the Women’s Rugby World Cup. Fans can observe how forwards secure possession while backs drive attacking plays, making matches exciting and dynamic. Recognising these roles also highlights standout players in England Rugby Women, Wales Rugby Women, and Scotland Rugby Women.
Each rugby position in women’s rugby requires a balance of skill, fitness, and tactical awareness. Forwards dominate scrums and lineouts, while backs focus on creating scoring opportunities and maintaining defensive structure. Awareness of these rugby positions makes following rugby fixtures and keeping up with rugby scores much more enjoyable. Fans gain a deeper understanding of the game’s strategy and the contributions of individual players in critical moments.
Position-Specific Skills and Team Strategy
Each rugby position demands specific skills, physical attributes, and tactical understanding. Forwards require power, endurance, and scrummaging technique, while backs excel in speed, vision, and precise passing. Understanding rugby positions enables both players and fans to appreciate why certain individuals thrive in their roles, whether in domestic leagues, international matches, or during the Rugby World Cup final.
Rugby positions also define team strategy and cohesion. Forwards and backs must coordinate seamlessly during scrums, rucks, mauls, and open play. Observing how each rugby position interacts in real-time highlights the complexity of the game and the importance of each role. Following BBC Sport Rugby coverage becomes more insightful when fans can identify which rugby positions are making crucial contributions to the team’s performance.
Conclusion
Rugby positions form the backbone of rugby union, shaping both individual roles and overall team performance. Understanding these positions allows players to improve their gameplay and fans to enjoy matches with greater insight. Following rugby today, keeping track of rugby scores, and watching events like the Rugby World Cup 2025 or Women’s Rugby World Cup becomes far more engaging when rugby positions are clearly understood.
Knowledge of rugby positions also enhances appreciation for the strategy, skill, and teamwork that define the sport. Whether watching England Rugby, Scotland Rugby, or domestic matches with Bath Rugby, understanding each rugby position allows fans to see how players influence the game. Rugby positions are essential not just for players but for anyone looking to fully enjoy the excitement and complexity of rugby union.
You may also read: Best Basketball Hoop for Sale UK: Adjustable, Portable & Durable Options for Every Player